GST Bill
How GST Bill in India has transformed the nation’s tax system?
The introduction of the much ambitious GST Bill in India came as a respite to its citizens as it is expected to curb corruption and introduce transparency in the tax system. This latest indirect GST tax has subsumed all the other existing indirect taxes, thereby reducing the cascading effects of tax duties that were responsible for market inflation. Pitched as ‘One nation, one tax’,GST intends at benefiting everybody in the country and affective none adversely. However, it will take some time before anything could be said about the implementation of this tax; whether GST is a miracle or a mirage. Here is more on this most sought after regime.
The need for GST bill.
Prior to the implementation of Goods and Services Tax or GST Bill in India, taxpayers had to pay multiple taxes on goods and services. The complex and confusing tax system used to give way to corruption, hence leading to problems for the government.Among the several included taxes that the traders, manufacturers, and at times commoners, etc. were bound to pay before GST included:
- Sales Tax: Levied on the sales of goods and was divided into Inter-State Sale, Sale during import/export and Intra-State sale.
- Service Tax: This included tax on paid services like telephone, advertising, financial assistance, consultancy, health, etc.
- Value Added Tax: It was the additional tax paid to the state government. Its rate was decided depending on the state and the type of item.
- Custom Duty and Octroi Tax: Levied on imported goods and the tax was paid at country’s port of entry. The tax rate differed as per the nature of goods.
- Excise Duty: Also termed as Central Value Added Tax, this indirect tax was levied on goods produced in the country.
- Anti-Dumping Duty: This tax was levied by the Central Government on the goods that were exported to other nations at a price comparably lower than the original cost.
What is GST Bill?
As you already know, a bill is a draft of proposed law that is escalated to the Parliament for healthy discussion followed by its approval. Once passed, the bill becomes an act and is implemented throughout the country and the same holds for GST Bill in India as well. After years of speculations and marathon discussions, both the houses of the parliament finally passed four legislations on 6th April 2017 – The Central GST Bill, 2017; The Integrated GST Bill, 2017; The GST (Compensation to States) Bill, 2017; and The Union Territory GST Bill, 2017. This led to the implementation of the much talked about Goods and Services Tax (GST) from July 1, 2017. The GST bill is hence now transformed to the GST ACT and is being followed under full constitutional rights all over the country.
Just to enhance your knowledge, GST is the One Hundred and Twenty Second (122nd) Amendment Bill of the Constitution of India. It is a comprehensive indirect tax that subsumes all the indirect taxes levied on manufacturing, sales, as well as consumption of goods and services all across the nation.It has now replaced all the indirect taxes levied by the Central and State government, respectively, on goods and services.
Components of GST
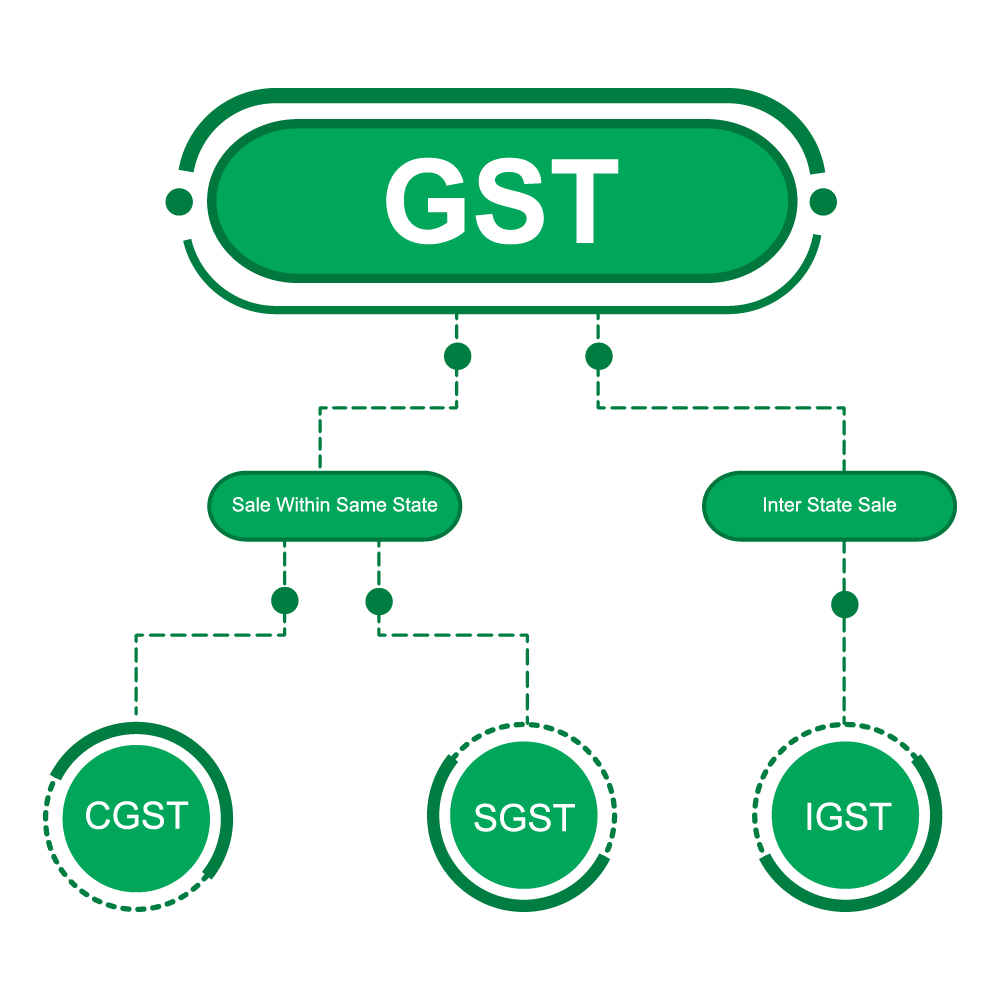
Various forms of GST have been introduced under the latest GST act. These include:
- State GST or SGST: Handled by the state government, this subsumes all the taxes collected under the state provision.
- Central GST or CGST: Handled by the central government, this tax is imposed on Intra State supplies of goods and services by the central government.
- Integrated GST or IGST: This tax bill is levied on the all the Inter-state supplies of goods and/or services. It is applicable in cases of import and export of goods and/or services into and from India. The tax thus collected under IGST is shared between state and central government.
- Union Territory GST or UGST: This particular GST bill intends to collect tax on every goods and services supply in the union territories.It makes up for the absence of legislature and has properties similar to that of SGST. The UGST is applied to Chandigarh, Lakshadweep, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands; all being the union territories of India
To understand all these GST taxes, namely, CGST, SGST and IGST and identify the conditions that make them applicable, it is important to know whether the transaction is an intra-state or inter-state supply.
Intra-State Goods or Services supply
This occurs when the location of the supplier and the buyer is in the same state. In this type of transaction, the seller is required to collect from the buyer, both Central GST and State GST. As is obvious, while CGST gets collected with Central Government, the State Government acquires the SGST. 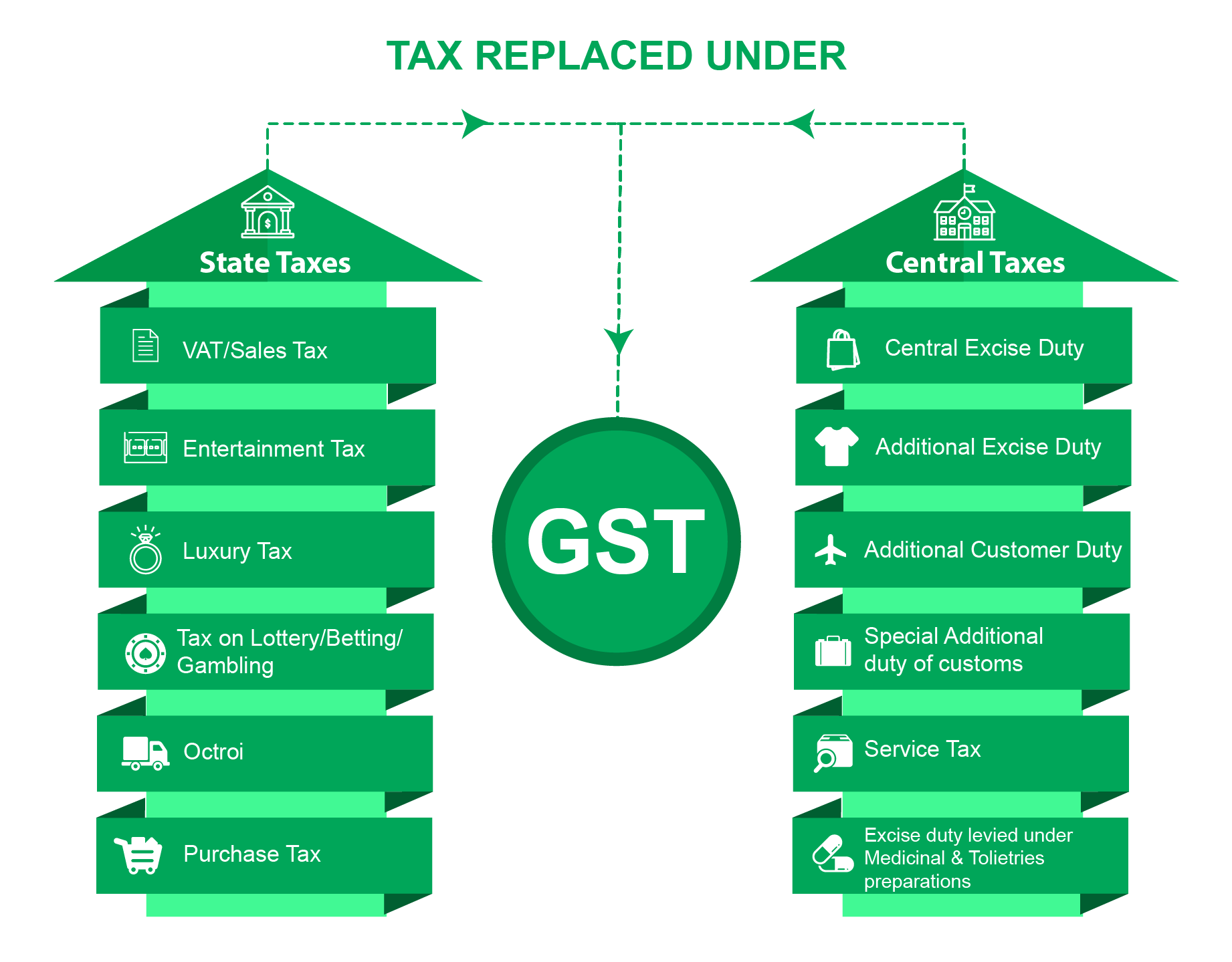
Inter-State Goods or services supply
When the location of the supplier and the place of supply (or buyer) are both in different states, an inter-state supply of goods and/or services takes place. IGST is also levied in the instances of import or export of goods or services or when goods or services are supplied to or by a SEZ unit.In all such types ofGST transactions, the seller collects IGST from the buyer.
Examples
The image below gives a pictorial representation of the working of Dual GST Model within a state. Note how State GST and Central GST are being applied. 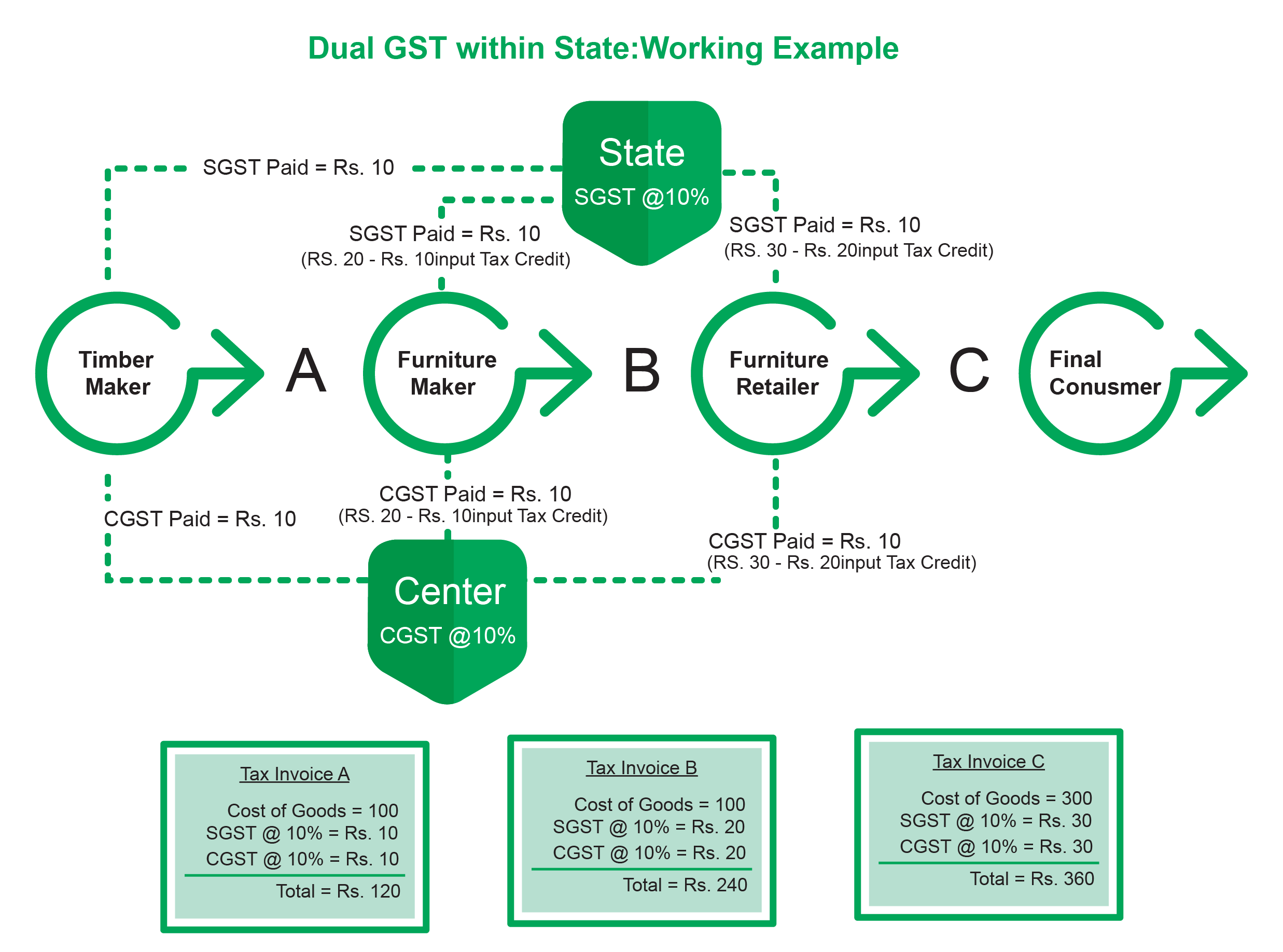
The image below depicts a pictorial representation of the IGST model for transactions between states. Observe the role of the three GST taxes -IGST, SGST and CGST. 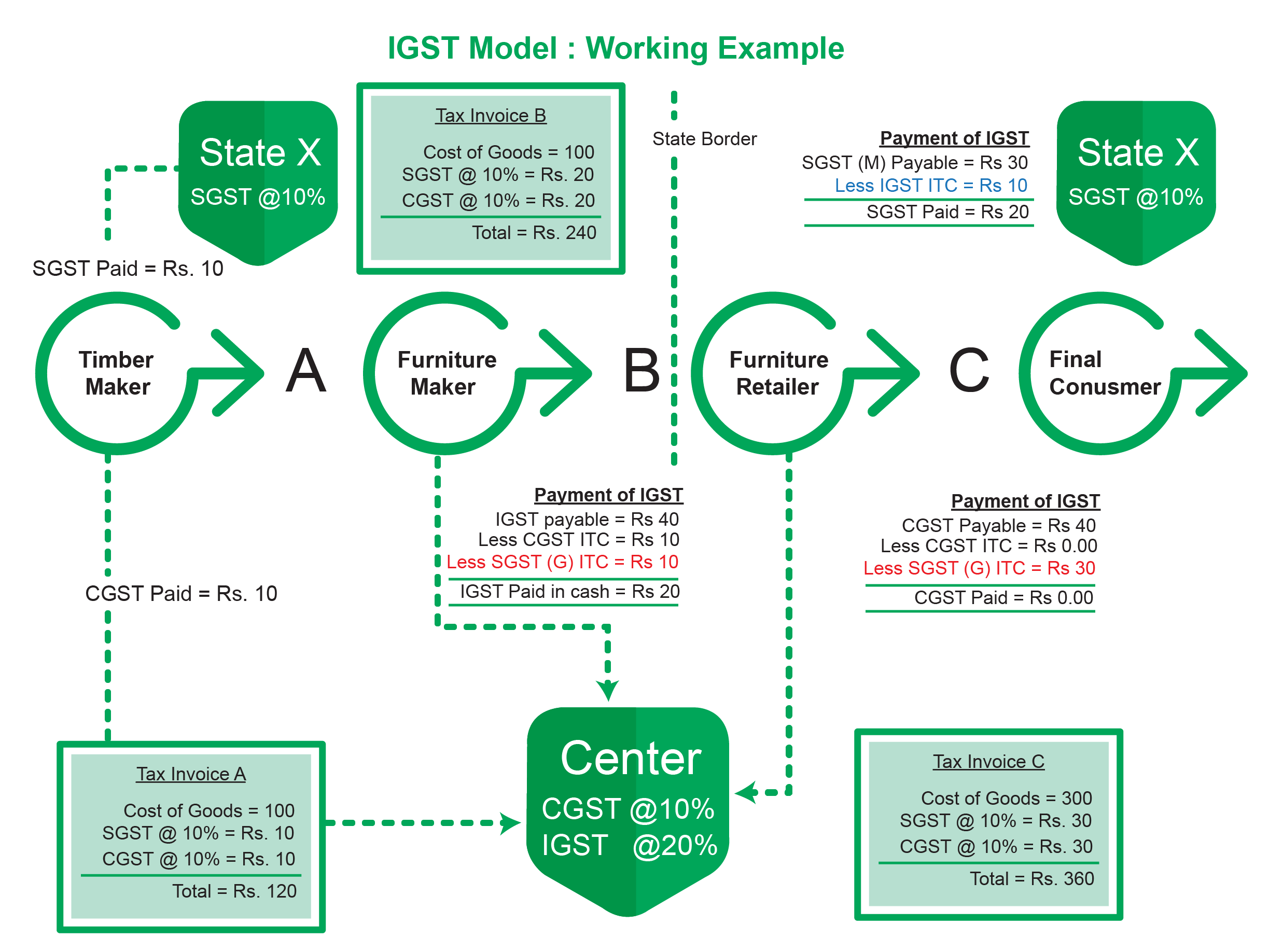
GST Tax Slabs and the contained items
Since long, the speculations were ripe about the tax slabs to be introduced under GST. There were uncertainties regarding the number of taxes levied, whether it will be a single one or multiple, depending on the goods and services offered. With the implementation of the GST Bill, all such confusions have now been answered. To be precise, the government of India has kept 1211 items under different tax slabs depending on their respective categories. Here is a brief description of which item/service, etc. goes to which slab under GST.
5% GST
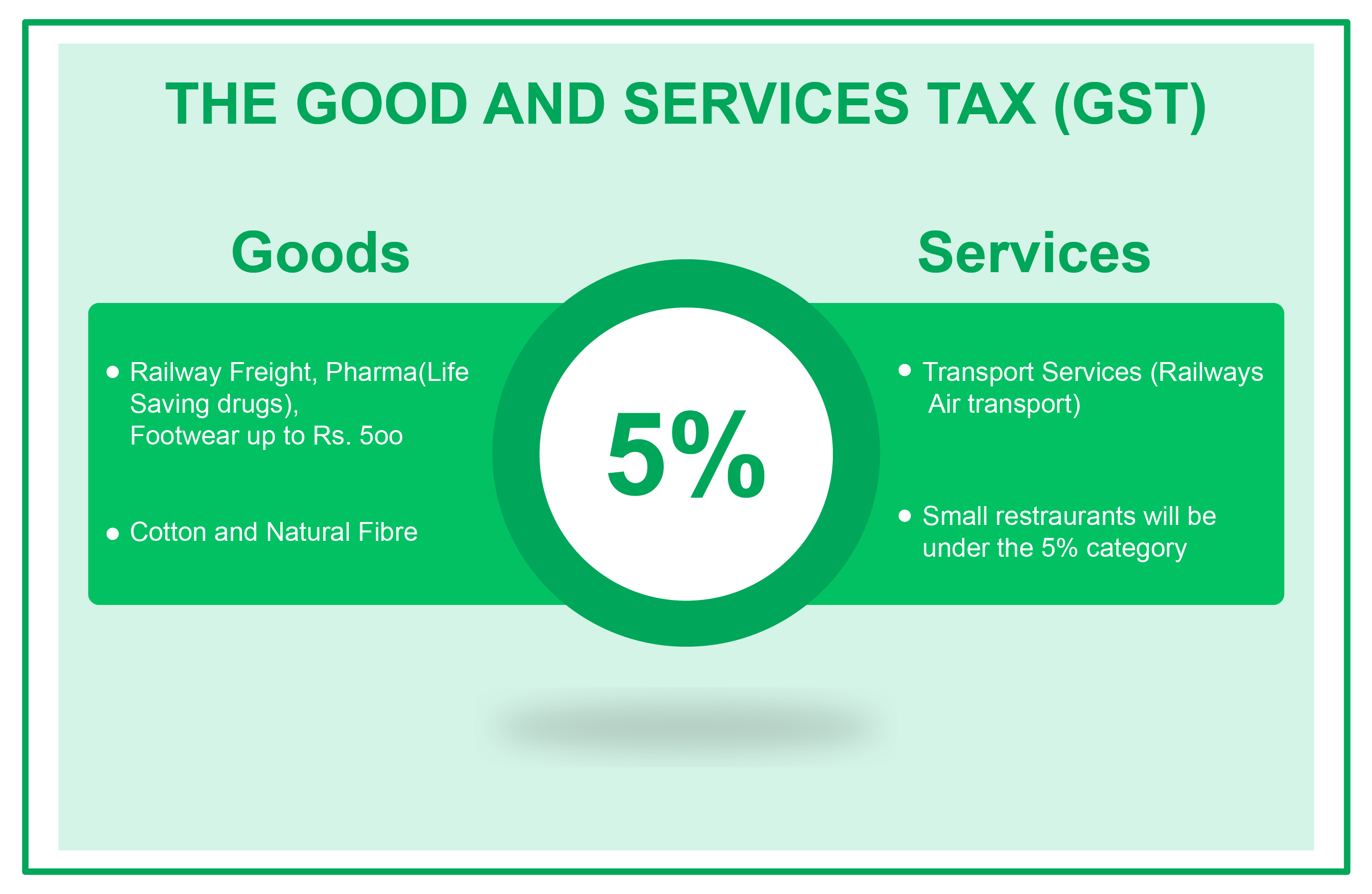
Besides, other items that have been accommodated under 5% GST tax slab include packaged food items, frozen vegetables, medicines, apparel below Rs 1000, footwear below Rs 500, Postage or revenue stamps, Branded food, fibre products like mats, pouches, wallets, skimmed milk powder, dried tamarind, walnuts, cashew nuts, Rosaries and prayer beads, Cotton quilts under Rs 1000 per piece, corals, and so on. As for services covered under the 5% GST tax bracket include railways and air transport, small restaurants and textile job work. For the very first time, the textile industry has been made to pay 5% GST tax across the manufacturing chain. Till now, this industry was completely tax free.
12% GST
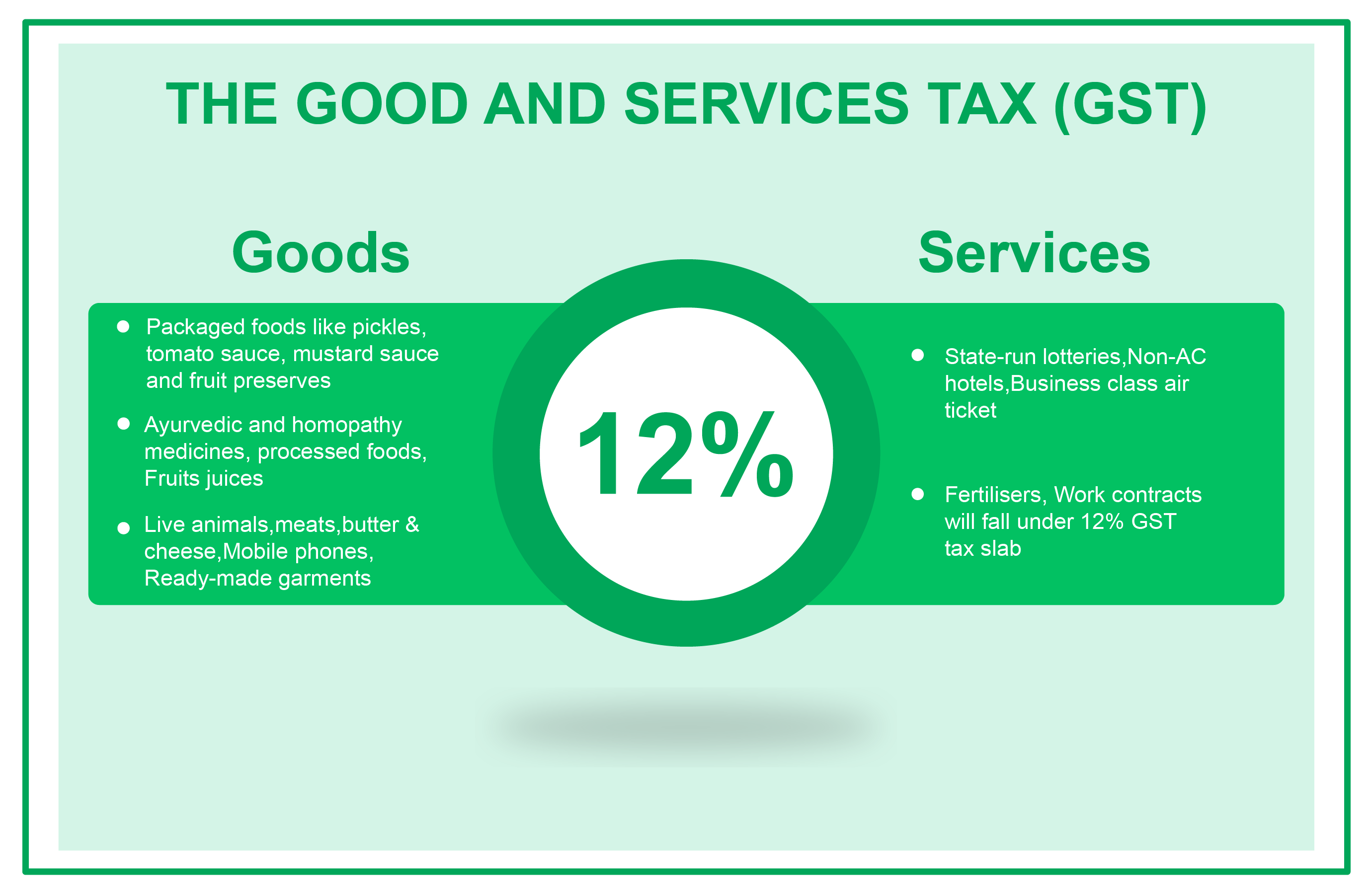
Goods that have been accommodated under 12% GST tax slab include eatables like packaged butter, cheese, ghee and dry fruits, frozen meat products,All diagnostic kits and reagents, games like playing cards, chess board, carom board, board games, like Ludo, etc., rubber band, Wood, stone, metals,marble idols,cotton quilts above Rs 1000 per piece, Table, kitchenware, cake servers, fish knives, spectacles, porcelain items, ornamental articles,animal carving items, sprinklers, bells, gongs, and so on. Among the services, business class air ticket, Non-AC hotels, State-run lotteries, fertilisers and work contracts fall under 12% GST tax structure.
18% GST
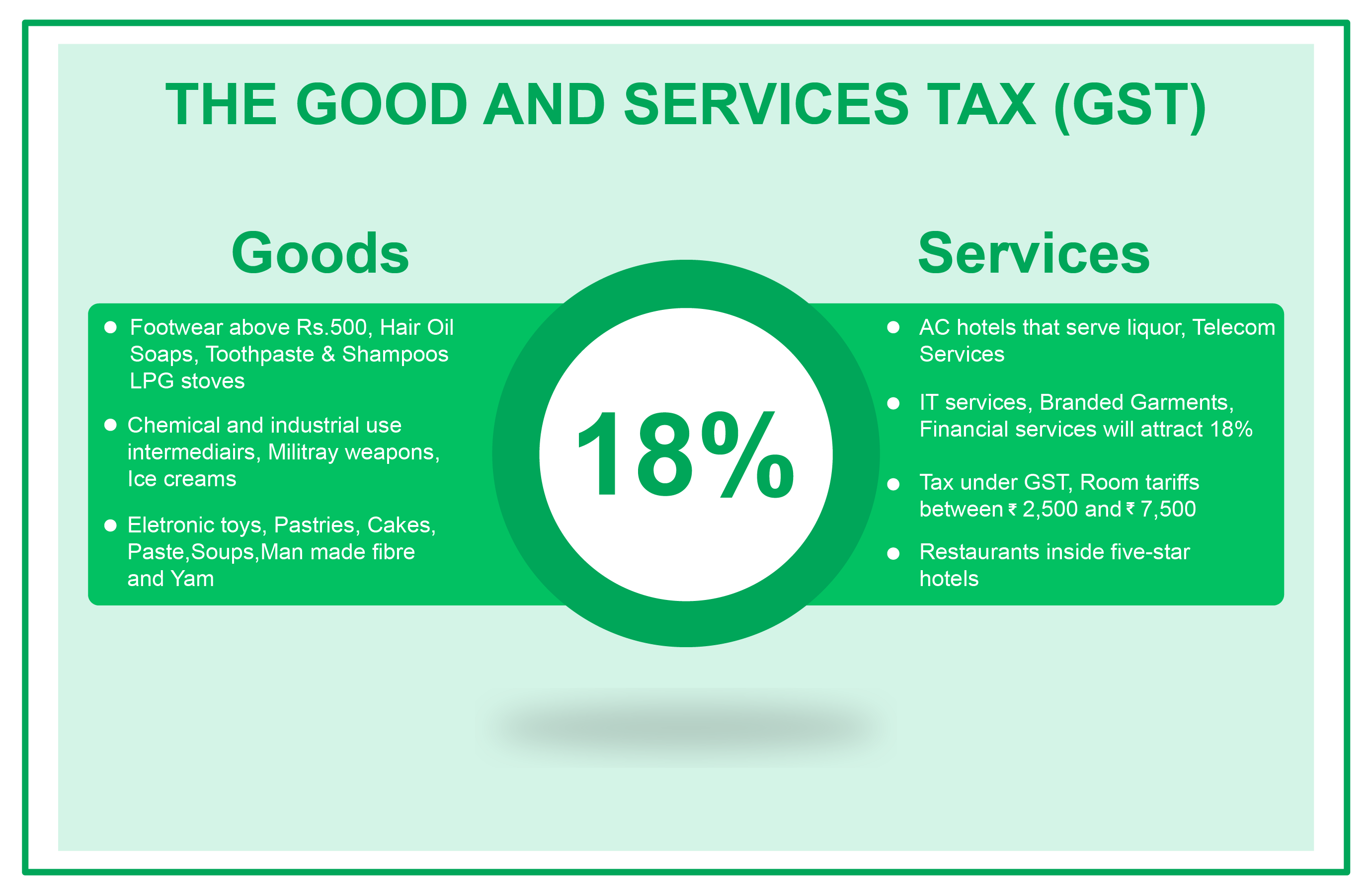
The Government of India has kept most of the items under this slab, here are few of them. Some common items include footwear above Rs 500, Trademarks,software, Computer monitors(up to 20 inch),camera, speakers,flavoured refined sugar, All types of biscuits, preserved vegetables, jams, sauces, soups,envelopes, tampons, Optical Fiber, Swimming pools and padding pools, Bamboo furniture, steel products, mixed condiments and seasonings,Rice rubber rolls,Kitchen gas lighters, tissues, mineral waters, and more.
Services that come under 18% GST tax slab include financial services, branded garments, AC hotels that offer liquor, IT services, Telecom services, Restaurants inside 5-star hotels, Room tariffs that fall under Rs 2,500 to Rs, 7,500 bracket, and branded garments.
28% GST
Finally, the items that come under 28% GST tax slab comprise , waffles and wafers coated with chocolate, molasses, chocolate not containing cocoa,Bidis, pan masala, deodorants, hair shampoo, sunscreen, ceramic tiles, washing machine, vacuum cleaner, automobiles, motorcycles, aircraft for personal use, ATM, vending machines, Shaving creams, after shave, chewing gum, weighing machine, and so on. Services that fall under 28% GST bracket include hotels with room tariffs more than Rs 7,500. 5-star hotels, State authorized private-run lotteries, race club betting, and cinema.
Items with 0% GST Tax

Several items have still been exempted from the GST tax slabs and we hope they remain excluded. These items include eatables like fish, chicken,eggs butter, milk, curd, natural honey, fruits & vegetables, Prasad, sindoor, bangles, kajal, stamps, judicial papers, printed books newspapers,bones and horn cores, drawing and colouring books for children, khadi bought from village and Khadi industries stores, charkha, brooms, clay idols,human hair, and so on. As for services, lodges and hotels having tariff below Rs 1,000 and grandfathering services have been kept at 0% GST tax slab.
In addition, unsorted rough industrial diamonds have been charged 0.25% GST tax instead of 3%.
You can get the complete list of all the items included under different GST tax slabs on the official website of Central Board of Excise and Customs.Here is the link for the same.
Conclusion
This is just a brief description of Goods and Services Tax or GST from GInvoicing.com. If you are interested to get a detailed insight into the murkier details of this newly introduced GST tax then feel free to approach us any time. We are equally helping in enabling you provide services related to GST bill creation and everything related to it.
